What Is a Supercell? The Ultimate Guide to Nature’s Most Powerful Storms
Supercells are the most powerful and intriguing thunderstorms on the planet. With their rolling, rotating clouds, these storms capture the imagination of storm chasers and scientists alike. But what exactly is a supercell, and why are they so important to understand?
What Sets a Supercell Apart
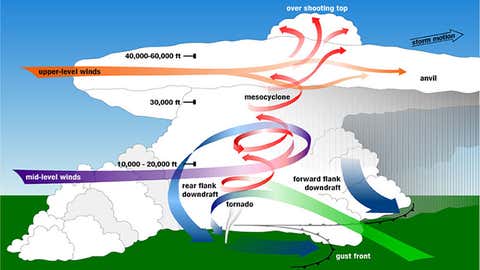
A supercell is a unique type of thunderstorm, distinguished by a rotating updraft known as a mesocyclone. This rotation makes the supercell far more organized and persistent than typical thunderstorms, often lasting for hours and traveling for hundreds of miles. Whereas regular storms may come and go quickly, supercells have the energy to maintain themselves and produce severe weather—including tornadoes, giant hail, and damaging winds.
According to Weather.com’s explainer on supercell thunderstorms, the secret behind a supercell’s power lies in wind shear. When wind changes speed or direction with height, it creates a "tube" of rotating air. If this is ingested by a developing storm, the updraft tilts it upright, forming the mesocyclone at the core of a supercell. This powerful updraft is what sets these storms apart from all others.
The Ingredients of a Supercell
For a supercell to develop, several key atmospheric conditions must come together:
- Moisture: Fuels strong updrafts.
- Instability: Allows air to rise rapidly.
- Wind Shear: Creates and maintains the rotating mesocyclone.
This scientific breakdown of supercells highlights how these storms need just the right mix to form. Classic supercells produce tornadoes and hail. High-precipitation supercells make tornadoes hard to spot because of heavy rain. Low-precipitation supercells often showcase striking cloud features with less rain.
Why Are Supercells So Dangerous?
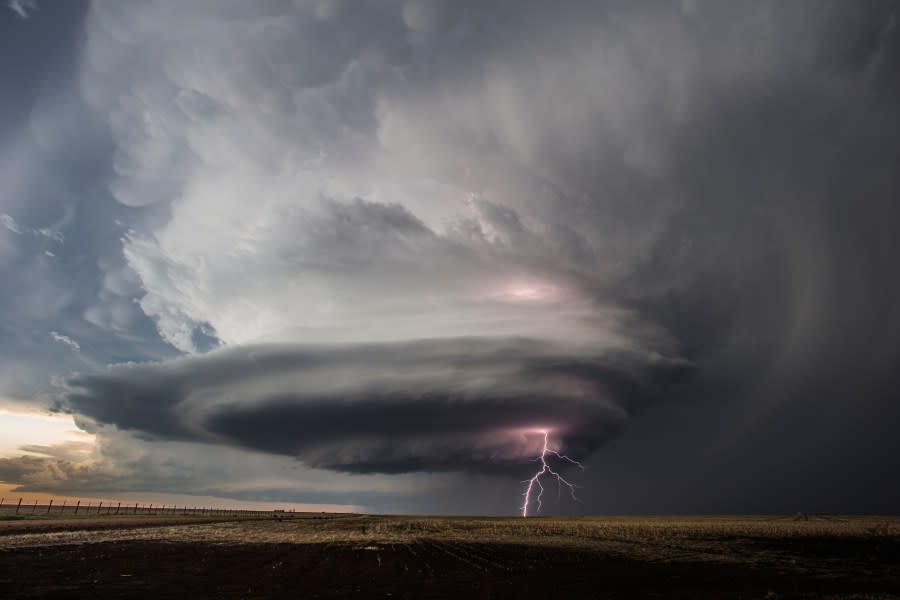
Supercells are responsible for most of the world’s strong, long-track tornadoes. Not every supercell will spawn a tornado, but the ones that do can produce some of the most destructive forces on Earth. Besides tornadoes, these storms frequently unleash hail large enough to dent cars and ruin roofs, flashes of intense lightning, flash flooding, and winds strong enough to topple trees and power lines.
High precipitation (HP) supercells are considered particularly hazardous. Rain can hide tornadoes within their core, making danger hard to see until it’s too late. Always take severe weather warnings seriously, especially if a supercell is in your area.
Supercells Versus Other Thunderstorms
While some storms can cluster together to form larger systems—known as mesoscale convective systems (MCS)—a supercell usually dominates the region by itself. You can read more about how a group of storms behaves in this article on mesoscale convective systems. In contrast, the rotating updraft at the heart of a supercell makes it the "king" of severe weather events.

How to Stay Safe When a Supercell Threatens
If a supercell forms in your area, it’s important to act quickly:
- Stay informed by monitoring local weather alerts.
- Have a plan to seek shelter, ideally in a basement or interior room away from windows.
- Be aware that hail and strong winds can arrive before you see a tornado.
- Do not rely solely on sight—tornadoes can be hidden by rain in HP supercells.
Meteorologists use radar to detect the rotation signatures inside supercells, helping issue timely warnings. Your best defense is preparedness and attention to official updates.
In Conclusion
Supercells are awe-inspiring but highly dangerous weather systems. Understanding what makes a supercell unique can help you recognize the risks and take action to stay safe. If you want to explore more about the science and impacts of these remarkable storms, check out the comprehensive guide on Weather.com and gain further insights into their formation and hazards from KXAN's explanation.
Stay alert, stay prepared, and always respect the power of a supercell.